Iron »
PDB 3pcq-3puq »
3pi8 »
Iron in PDB 3pi8: Site-Specific Glycosylation of Hemoglobin Utilizing Oxime Ligation Chemistry As A Viable Alternative to Pegylation
Protein crystallography data
The structure of Site-Specific Glycosylation of Hemoglobin Utilizing Oxime Ligation Chemistry As A Viable Alternative to Pegylation, PDB code: 3pi8
was solved by
V.S.Bhatt,
T.J.Styslinger,
N.Zhang,
P.G.Wang,
A.F.Palmer,
with X-Ray Crystallography technique. A brief refinement statistics is given in the table below:
| Resolution Low / High (Å) | 38.06 / 2.20 |
| Space group | P 21 21 21 |
| Cell size a, b, c (Å), α, β, γ (°) | 61.977, 72.995, 128.483, 90.00, 90.00, 90.00 |
| R / Rfree (%) | 22.6 / 28.1 |
Iron Binding Sites:
The binding sites of Iron atom in the Site-Specific Glycosylation of Hemoglobin Utilizing Oxime Ligation Chemistry As A Viable Alternative to Pegylation
(pdb code 3pi8). This binding sites where shown within
5.0 Angstroms radius around Iron atom.
In total 4 binding sites of Iron where determined in the Site-Specific Glycosylation of Hemoglobin Utilizing Oxime Ligation Chemistry As A Viable Alternative to Pegylation, PDB code: 3pi8:
Jump to Iron binding site number: 1; 2; 3; 4;
In total 4 binding sites of Iron where determined in the Site-Specific Glycosylation of Hemoglobin Utilizing Oxime Ligation Chemistry As A Viable Alternative to Pegylation, PDB code: 3pi8:
Jump to Iron binding site number: 1; 2; 3; 4;
Iron binding site 1 out of 4 in 3pi8
Go back to
Iron binding site 1 out
of 4 in the Site-Specific Glycosylation of Hemoglobin Utilizing Oxime Ligation Chemistry As A Viable Alternative to Pegylation
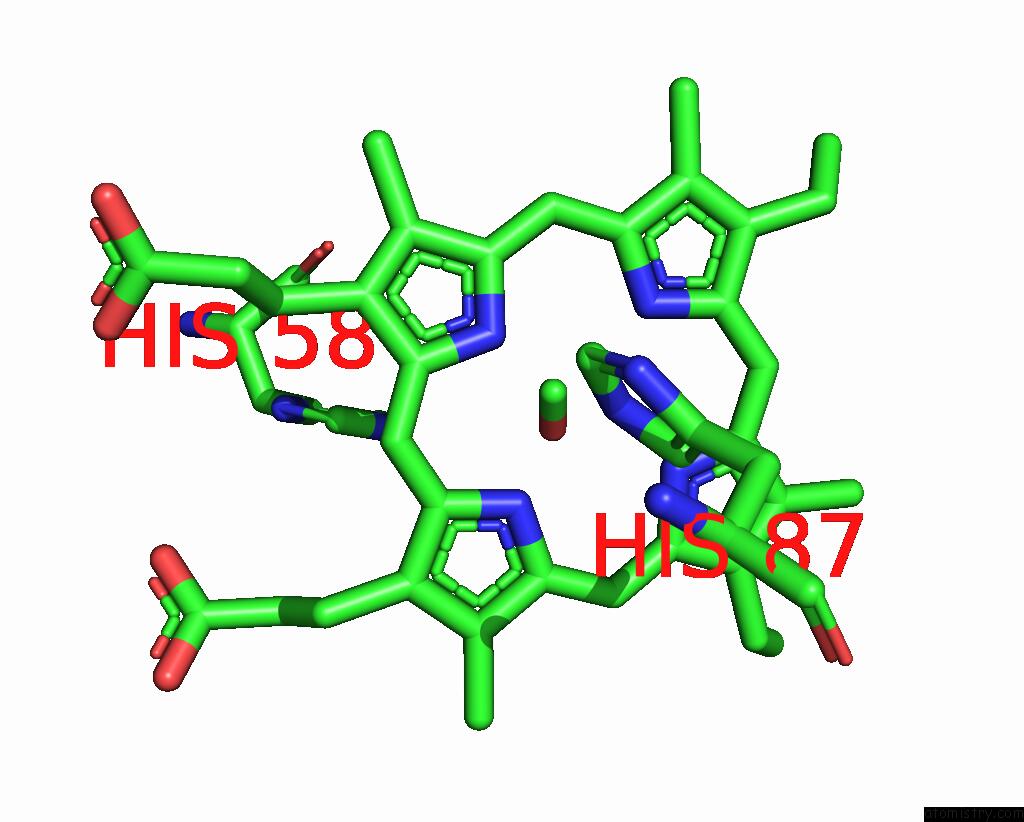
Mono view
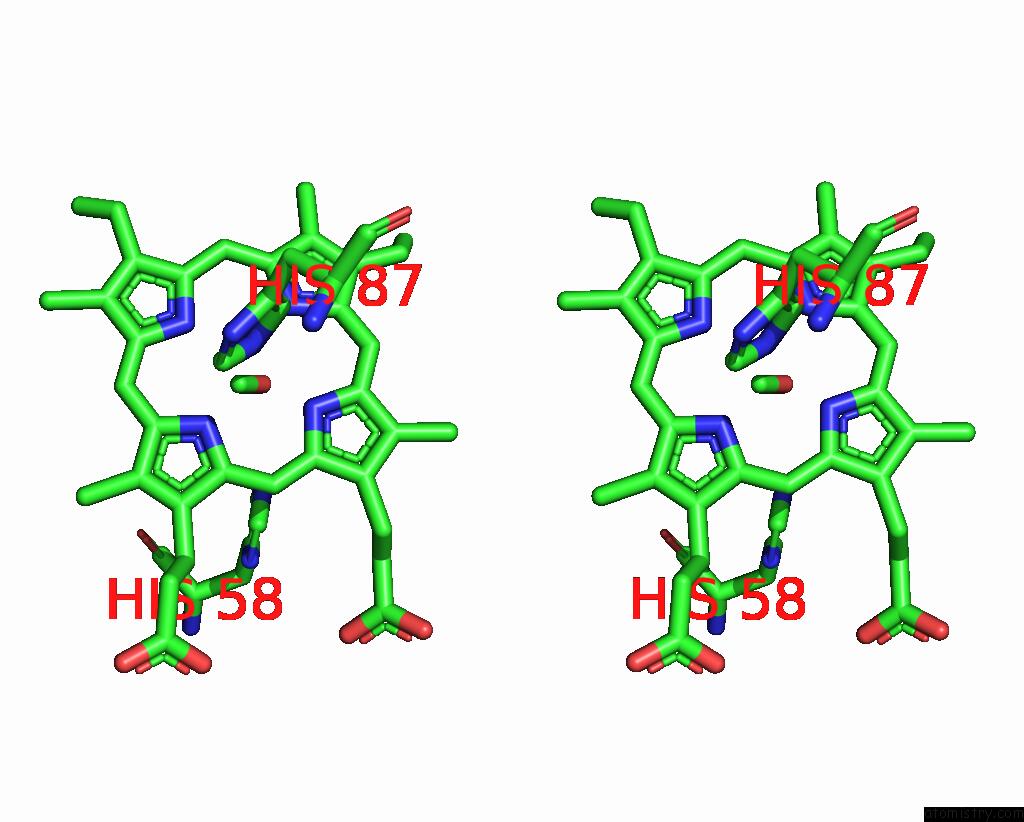
Stereo pair view

Mono view

Stereo pair view
A full contact list of Iron with other atoms in the Fe binding
site number 1 of Site-Specific Glycosylation of Hemoglobin Utilizing Oxime Ligation Chemistry As A Viable Alternative to Pegylation within 5.0Å range:
|
Iron binding site 2 out of 4 in 3pi8
Go back to
Iron binding site 2 out
of 4 in the Site-Specific Glycosylation of Hemoglobin Utilizing Oxime Ligation Chemistry As A Viable Alternative to Pegylation
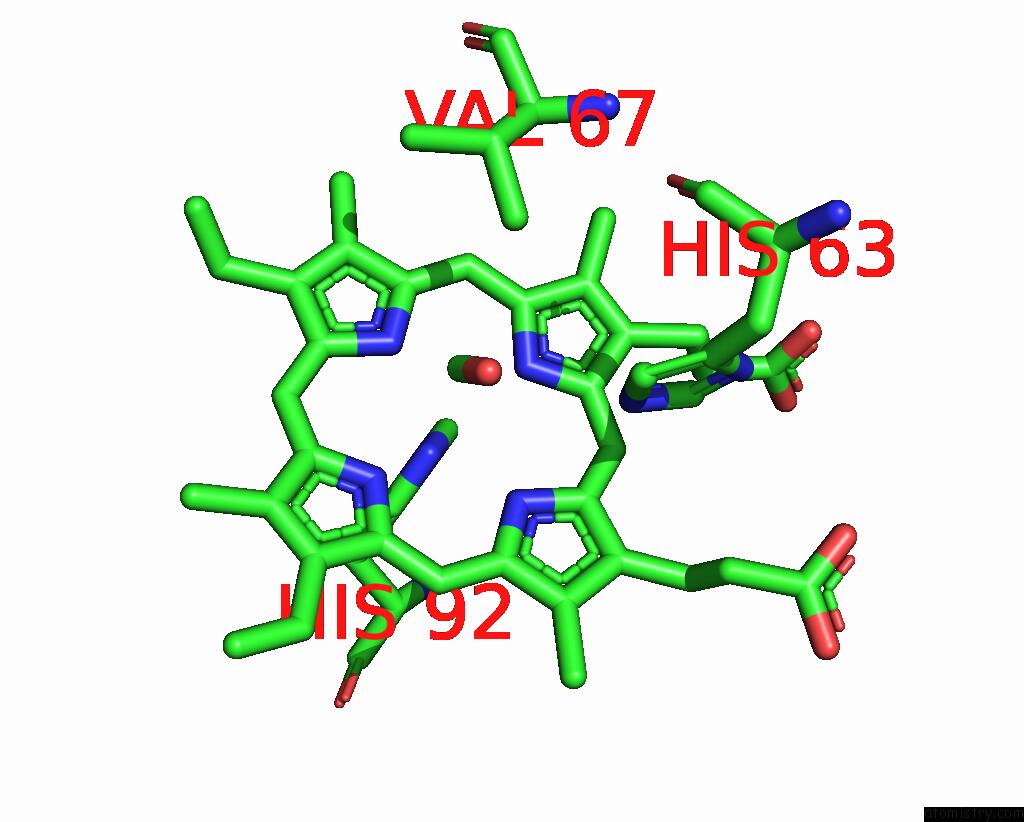
Mono view
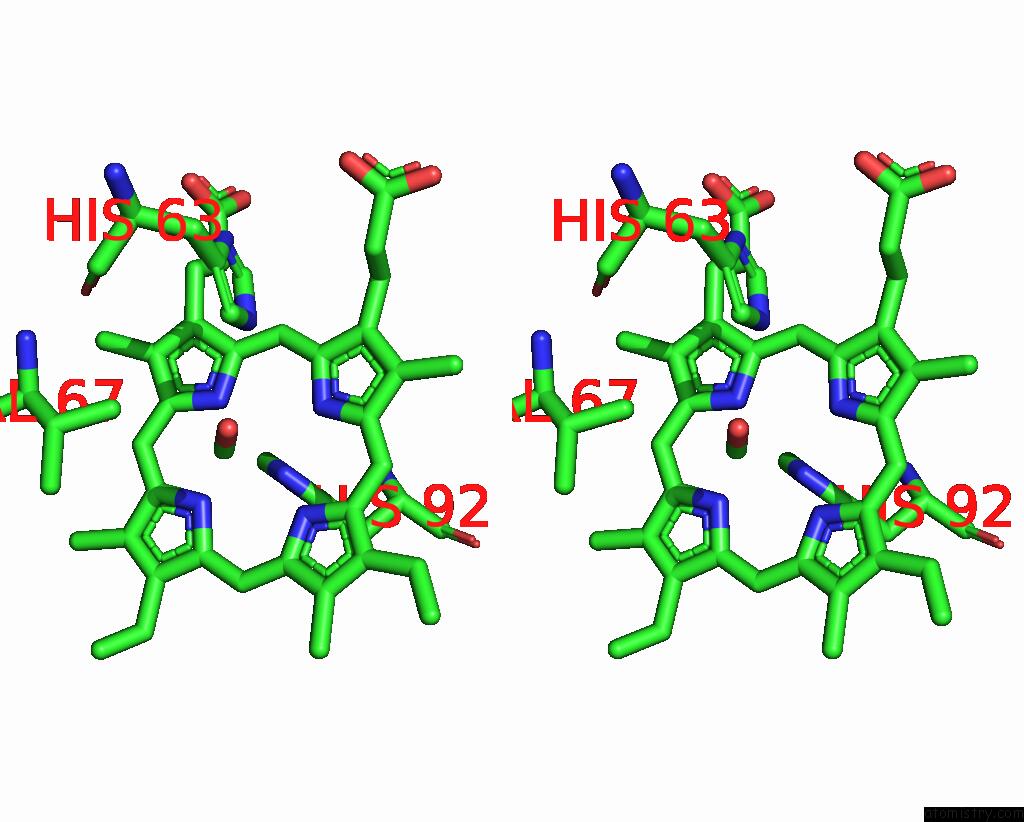
Stereo pair view

Mono view

Stereo pair view
A full contact list of Iron with other atoms in the Fe binding
site number 2 of Site-Specific Glycosylation of Hemoglobin Utilizing Oxime Ligation Chemistry As A Viable Alternative to Pegylation within 5.0Å range:
|
Iron binding site 3 out of 4 in 3pi8
Go back to
Iron binding site 3 out
of 4 in the Site-Specific Glycosylation of Hemoglobin Utilizing Oxime Ligation Chemistry As A Viable Alternative to Pegylation
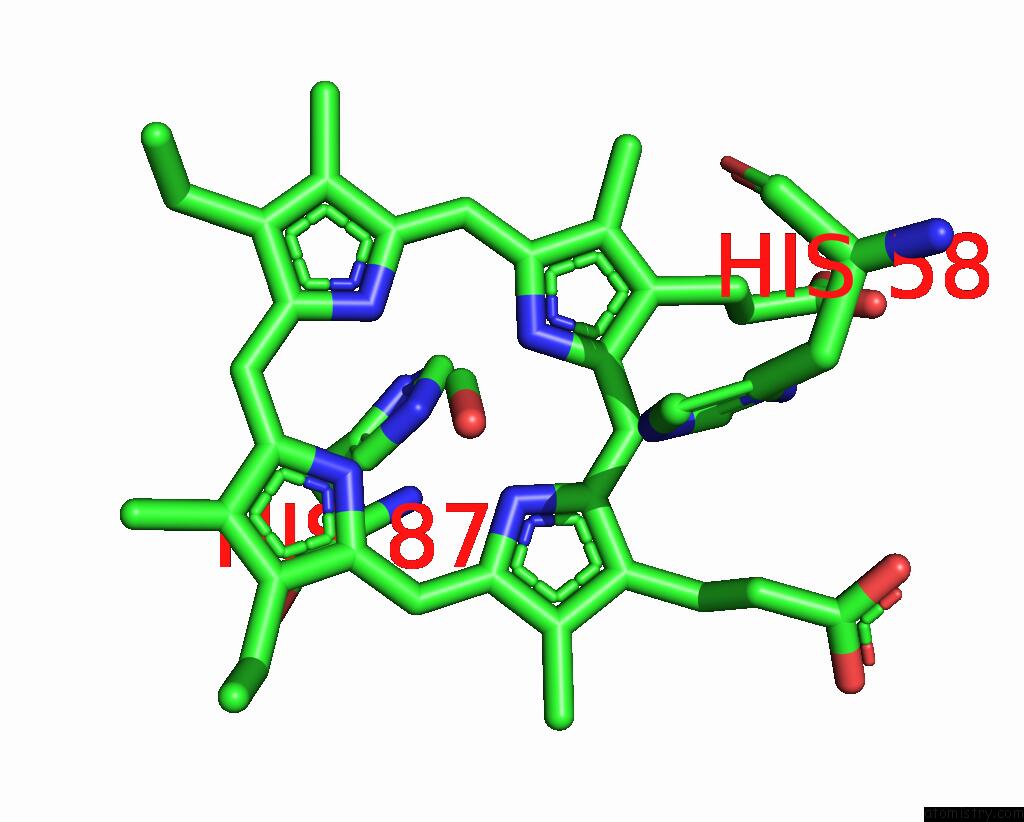
Mono view
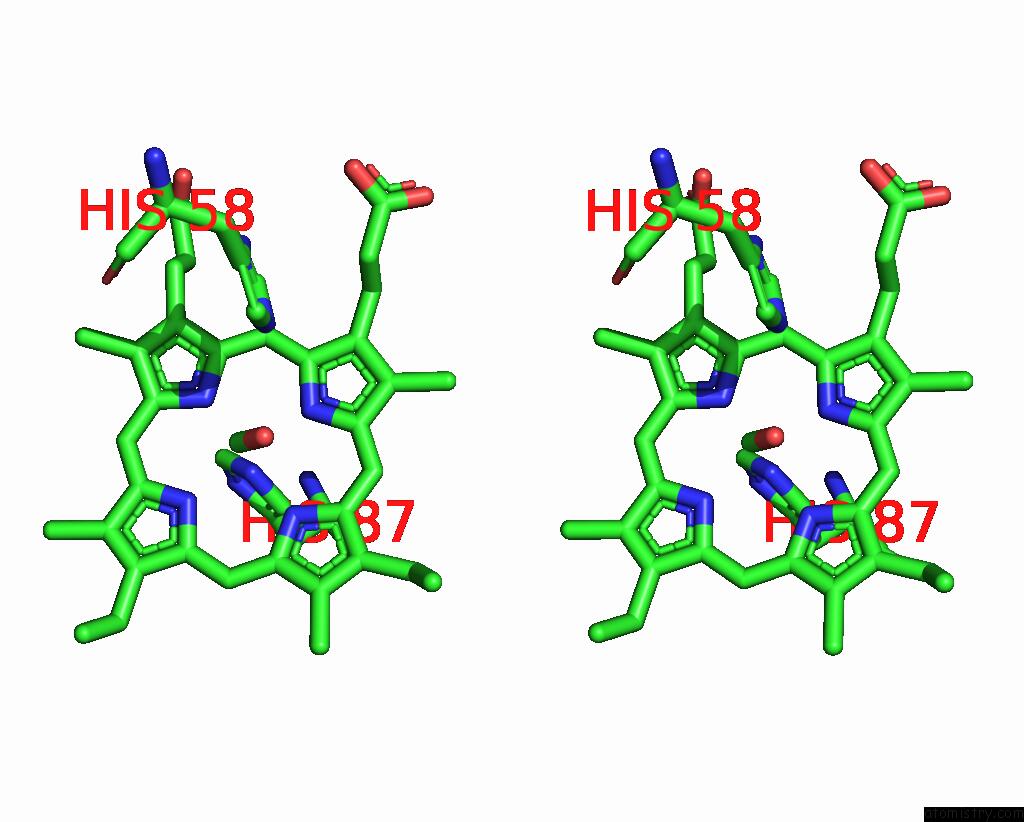
Stereo pair view

Mono view

Stereo pair view
A full contact list of Iron with other atoms in the Fe binding
site number 3 of Site-Specific Glycosylation of Hemoglobin Utilizing Oxime Ligation Chemistry As A Viable Alternative to Pegylation within 5.0Å range:
|
Iron binding site 4 out of 4 in 3pi8
Go back to
Iron binding site 4 out
of 4 in the Site-Specific Glycosylation of Hemoglobin Utilizing Oxime Ligation Chemistry As A Viable Alternative to Pegylation
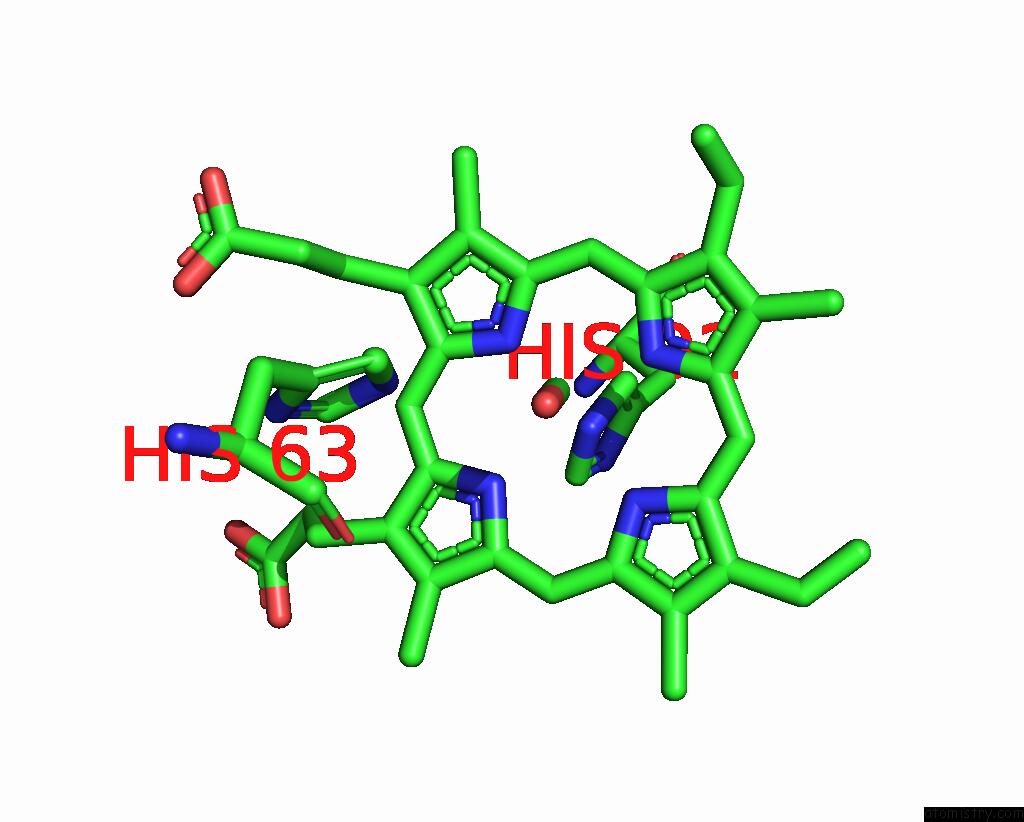
Mono view
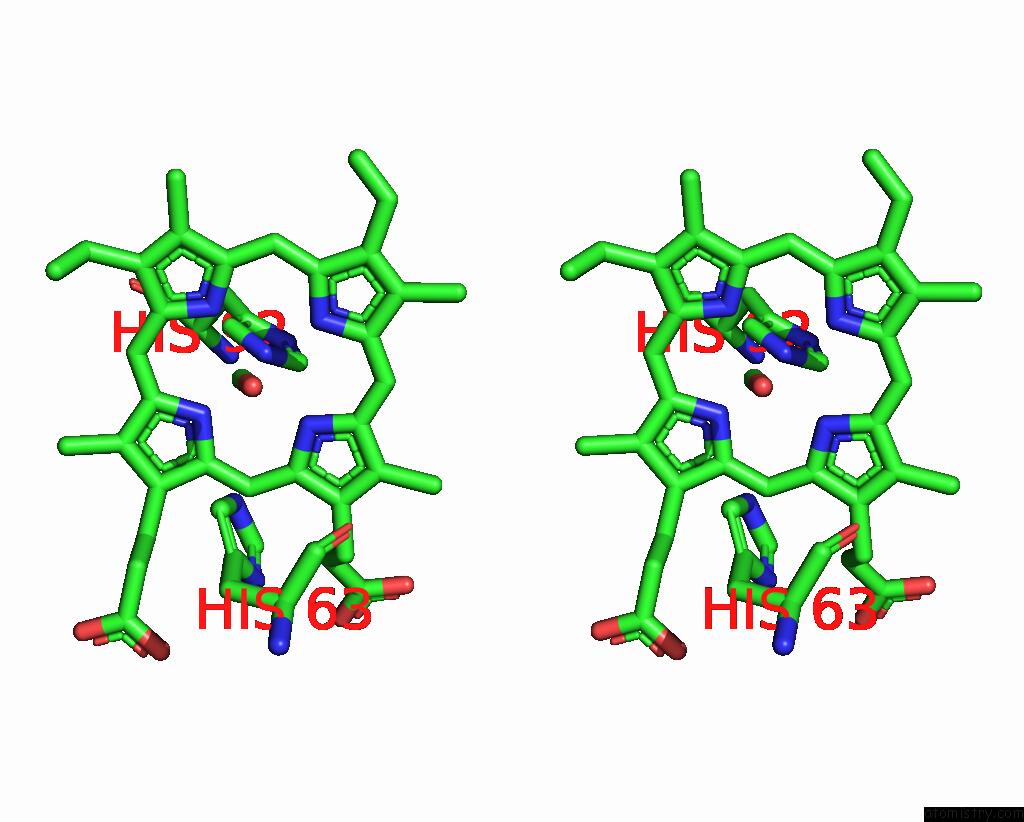
Stereo pair view

Mono view

Stereo pair view
A full contact list of Iron with other atoms in the Fe binding
site number 4 of Site-Specific Glycosylation of Hemoglobin Utilizing Oxime Ligation Chemistry As A Viable Alternative to Pegylation within 5.0Å range:
|
Reference:
V.S.Bhatt,
T.J.Styslinger,
N.Zhang,
P.G.Wang,
A.F.Palmer.
N/A N/A.
Page generated: Tue Aug 5 05:44:32 2025
Last articles
Fe in 3WECFe in 3WCU
Fe in 3WCT
Fe in 3WCP
Fe in 3WCQ
Fe in 3WC8
Fe in 3WAH
Fe in 3WAQ
Fe in 3W9C
Fe in 3W5U